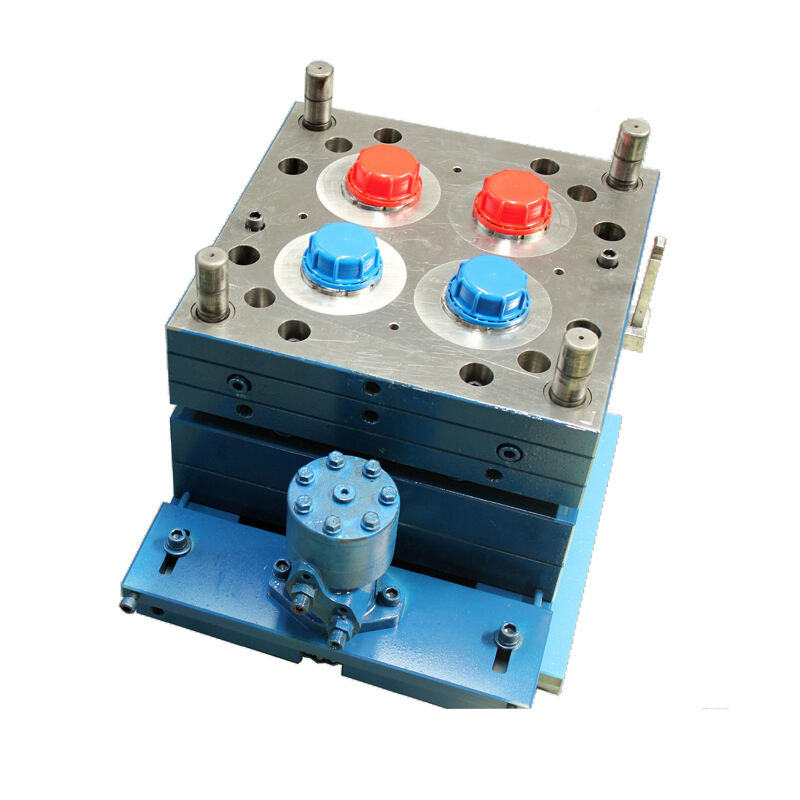
Ontwerpfase: DFM-gestuurde ontwikkeling van kunststof spuitgietmallen
Integratie van Design for Manufacturability (DFM) om kostbare herzieningen te voorkomen
Design for Manufacturability (DFM) integreert de haalbaarheid van productie vanaf het begin in de onderdeelgeometrie—waardoor kostbare aanpassingen later in het proces worden voorkomen. Het negeren van DFM leidt gemiddeld tot een budgetoverschrijding van 22%, voornamelijk als gevolg van correcties aan de gereedschappen na productie (PwC, 2022). De kernprincipes zijn:
-
Gelijke wanddikte (ideaal 1–3 mm) om inkortingsplekken te voorkomen en een uniforme koeling te waarborgen
-
Voldoende uittrekhoeken (≥1° per zijde) om betrouwbare uitschakeling zonder oppervlakteschade te mogelijk te maken
-
Minimale ondercuts , waardoor de behoefte aan schuifstukken en uitwerkers die de matrijsarchitectuur compliceert, wordt verminderd of geëlimineerd
Wanneer vroegtijdig toegepast, vermindert DFM het aantal gereedschapswijzigingen met 30–50% en verkort het de time-to-market door het ontwerpdoel in lijn te brengen met de procescapaciteit.
Kern-/holte-indeling, koelsysteemplanning en plaatsing van uitwerkers in CAD
Strategische, op CAD gebaseerde planning is de basis voor thermische en mechanische stabiliteit. Belangrijke overwegingen zijn:
-
Uitlijning van kern/holte gehouden binnen een tolerantie van ±0,005 mm om een consistente onderdeeldikte te behouden en speling of onvolledige vulvulling (short shots) te voorkomen
-
Conformele koelkanalen , gepositioneerd op een afstand van 1,5× hun diameter vanaf de matrijsoppervlakken, verminderen de cyclusduur met tot wel 25% en minimaliseren vervorming
-
Plaatsing van uitwerkerpennen gekoppeld aan gebieden met lage spanning — gevalideerd via simulatie — om vervorming van het onderdeel of oppervlaktegebreken te voorkomen
Stroming van hars, drukverdeling en thermisch gedrag worden gesimuleerd voorheen bewerking begint, waardoor het risico op matrijsprestaties wordt verlaagd en het aantal fysieke proefiteraties wordt verminderd.
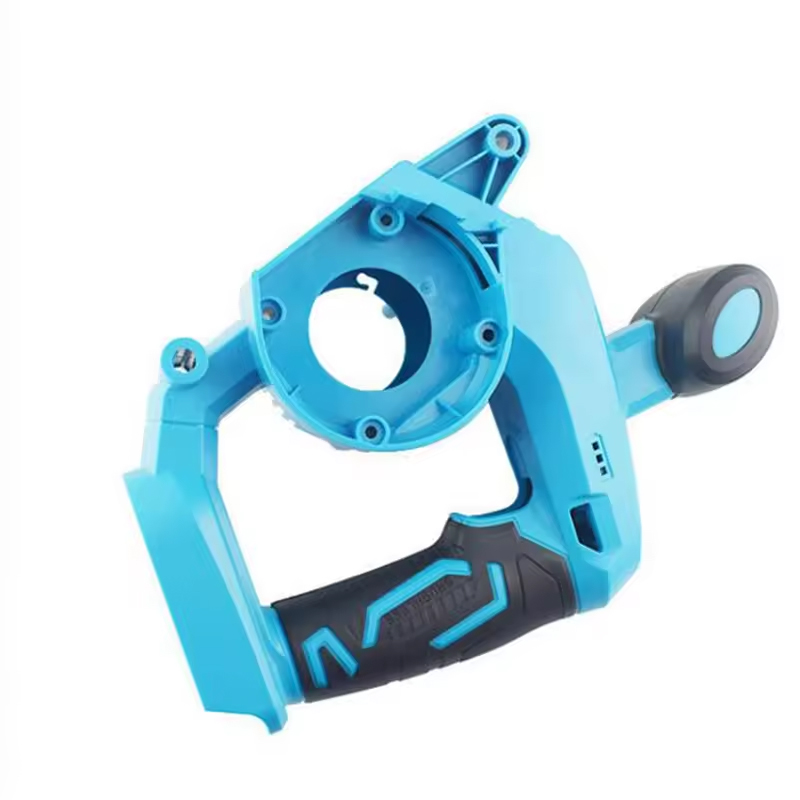
Matrijsconstructie: staalselectie en modulaire matrijsbasisassemblage
Afstemming van matrijsstaalsoorten (P20, H13, S7) op productievolume en schurende eigenschappen van de hars
Het kiezen van het juiste gereedschapsstaal maakt alle verschil voor de levensduur van matrijzen, hun kosten en hoe goed ze standhouden tijdens de werkelijke productie. Vooraf gehard P20-staal biedt een goede afweging tussen budget en taaiheid voor kleinere productierunners van minder dan ongeveer 100.000 cycli, vooral bij het verwerken van materialen zoals polypropyleen die de gereedschappen niet al te zwaar belasten. Wanneer fabrikanten een materiaal nodig hebben dat zware belastingen aankan, is H13 de standaardkeuze. Dit staal heeft doorgaans een hardheid van 45 tot 50 op de Rockwell-schaal en weerstaat temperatuurwisselingen veel beter, waardoor het ideaal is voor zeer grote productierunners van meer dan een half miljoen cycli, waarbij materialen zoals glasvezelversterkt nylon de gereedschappen echt gaan slijten. Bij toepassingen met corrosieve stoffen zoals PVC biedt S7-staal uitstekende dimensionale stabiliteit, hoewel het wel 15 tot 20 procent duurder is dan P20. Sectorexperts analyseerden in 2023 alle gevallen van storingen en kwamen tot een vrij opvallende conclusie: ongeveer twee derde van de vroege matrijsfouten onder zware omstandigheden was simpelweg het gevolg van een onjuiste combinatie van staalsoort en kunststofmateriaal.
Modulair matrijsbasisonderdeelontwerp voor snelle vervanging van inzetstukken en efficiënt onderhoud
Modulaire matrijsbases — gebouwd rond gestandaardiseerde, uitwisselbare inzetstukken voor kernen, holten en uitwerpsystemen — verminderen de wisseltijd met 40% ten opzichte van massieve ontwerpen. Voordelen omvatten:
-
Wisselbare onderdelen zonder uitschakelen , waardoor volledige vervanging van inzetstukken in minder dan twee uur mogelijk is
-
Gerichte reparaties , waardoor volledige demontage van de matrijs en de daarmee gepaard gaande verlies van kalibratie worden voorkomen
-
Iteratie met versiebeheer , wat snelle schaalvergroting of updates van familiematrijzen ondersteunt
Onderhoudslogboeken bij leveranciers van Tier-1 tonen aan dat modulaire systemen de jaarlijkse onderhoudskosten voor gereedschappen gemiddeld met $18.000 verlagen — voornamelijk door arbeidskosten voor machine-demontage te elimineren en stilstandtijd tot een minimum te beperken.
Precisiefabricage: CNC-bewerking en EDM voor kritieke matrijsfuncties
Hoog-nauwkeurige CNC-bewerking van matrijsoppervlakken en wanden met uittrekhoek (±0,005 mm)
De nieuwste 5-assige CNC-machines kunnen een positioneringsnauwkeurigheid van ongeveer 0,005 mm bereiken en produceren oppervlakteafwerkingen onder Ra 0,4 micron, zelfs bij moeilijk bewerkbare gereedschapsstaalsoorten. Deze specificaties zijn uiterst belangrijk om ervoor te zorgen dat holtes, kernen en die lastige uitwerpergebieden correct worden vervaardigd. De machine verwerkt hellende wanden, gecompliceerde vormen en de uiterst strakke toleranties die nodig zijn om te garanderen dat onderdelen correct worden uitgeworpen én er ook nog eens goed uitzien. Wanneer fabrikanten deze mate van reproduceerbare precisie bereiken, brengen ze minder tijd door aan handpolijsten en komen er geen spelingproblemen meer voor waarbij onderdelen niet perfect op elkaar passen. Bij grotere matrijzen of matrijzen die extreme nauwkeurigheid vereisen, betekent elke afwijking van meer dan 0,01 mm problemen op termijn: afgewezen onderdelen, montageproblemen of, nog erger, onderdelen die simpelweg niet functioneren zoals bedoeld. Daarom vertrouwen serieuze matrijsbouwers op CNC-technologie als hun standaardoplossing voor het maken van precisiematrijzen die voldoen aan strenge specificaties.
EDM-toepassingen voor dunwandige holtes, fijne structuren en elektrode-afhankelijke geometrieën
EDM omzeilt die vervelende geometrische problemen waar gewone bewerkingen simpelweg niet tegenop kunnen, vooral bij zeer harde stalen met een hardheid van meer dan 50 HRC, waarbij standaard snijgereedschappen ofwel geen toegang hebben tot de te bewerken gebieden ofwel te snel slijten. Sinker-EDM werkt wonders bij het maken van gecompliceerde 3D-vormen, extreem scherpe inwendige hoeken met een radius kleiner dan 0,1 mm en zelfs gedetailleerde oppervlakteafwerkingen zoals leerstructuurpatronen. Wire-EDM is weer iets anders: ideaal voor het maken van conische sleuven, slanke constructieribben en kwetsbare wanden die dunner zijn dan een halve millimeter. De medische-apparatuur- en micro-elektronica-industrie zijn sterk afhankelijk van EDM-technieken, aangezien de meeste kenmerken kleiner dan 1 mm deze op elektroden gebaseerde methoden vereisen. Wat EDM zo waardevol maakt, is de mogelijkheid om een buitengewone precisie van ±0,002 mm te bereiken, zonder mechanische belasting uit te oefenen of die vervelende warmtebeïnvloede zones te veroorzaken die traditionele bewerkingsmethoden plagen.
Validatie en kwalificatie: Polijsten, assemblage en T0/T1-bemonstering
Normen voor oppervlakteafwerking (SPI A–D), controle van ontluchting en pasvormcontroles
De oppervlakteafwerking voldoet aan de SPI A–D-normen om te voldoen aan functionele en esthetische vereisten:
-
SPI A (Klasse #1) : diamantpolijsten met korrelgrootte 12.000 voor optische helderheid (bijv. lenzen, lichtgeleiders)
-
SPI B (Klasse #2) : korrelgrootte 600–1.200 voor hoogglans consumeronderdelen
-
SPI C (Klasse #3) : steenafwerking met korrelgrootte 600 voor gestructureerde oppervlakken die grip of visuele diffusie vereisen
-
SPI D (Klasse #4) stralen met kralen voor een matte, industrieel-kwalitatieve afwerking
Ontluchtingskanalen worden gecontroleerd met rooktesten om de spelingen van 0,015–0,02 mm te verifiëren — waardoor gasinsluiting en brandvlekken worden voorkomen. Modulaire inzetstukken ondergaan pascontroles om een uitlijningstolerantie van <0,003 mm op de scheidingslijnen te garanderen, wat een vlaskleurvrije werking waarborgt.
T0-droogtest en T1-validatie van het eerste onderdeel met vervormings- en dimensionele analyse
T0 (droogtest) test valideert de mechanische en thermische gereedheid zonder hars:
- Uitwerktijd gesynchroniseerd tot ±0,1 s
- Temperatuurgradiënten tussen kern en vorm behouden binnen ΔT ≥5 °C
- Druk van het hydraulische systeem gestabiliseerd tot ±2 % van de ingestelde waarde
T1 (eerste spuitbeurt) validatie wordt uitgevoerd met het daadwerkelijke productiemateriaal. Gebruikte onderdelen worden met een CMM gescand tegen CAD-modellen, met metingen van:
- Vervormingsafwijking < 0,2 % van de nominale onderdeellengte
- Afmetingsconformiteit binnen ± 0,05 mm (in overeenstemming met ISO 20457-toleranties voor kunststof spuitgietmallen)
- Diepte van de gietpoortrest ≥ 0,1 mm
Strenge T0/T1-protocollen verminderen de nabewerking van mallen met 68 %, waardoor de kwalificatie en opvoering naar productie worden versneld (Plastics Today, 2023).
Klaar om uw ontwerp en ontwikkeling van kunststof spuitgietmallen te optimaliseren?
Het ontwerp en de fabricage van uw matrijs vormen de basis voor consistente, kosteneffectieve productie — het nemen van kortere routes bij DFM, precisiebewerking of validatie leidt tot vertragingen, nabewerking en een lagere kwaliteit van de onderdelen. Door DFM-best practices, hoogwaardige mallenmaterialen en strenge tests te integreren, verkrijgt u mallen die betrouwbare prestaties leveren, een kortere time-to-market mogelijk maken en een lagere totale eigendomskost genereren.
Voor op maat gemaakte oplossingen voor kunststof spuitgietmallen—ondersteund door DFM-expertise, geavanceerde CNC/EDM-vervaardiging en strikte validatieprotocollen—kies een partner met diepgewortelde expertise in mallentechniek. Onze decennia lange ervaring strekt zich uit over de medische, automobiel-, elektronica- en consumentengoederensector. Neem vandaag nog contact met ons op voor een vrijblijvend consult om uw maldesign te verfijnen, risico’s te verminderen en uw productietijd te verkorten. Laten we samen mallen bouwen die uw ontwerpvisie omzetten in tastbare succes.

 EN
EN
 AR
AR
 HR
HR
 CS
CS
 DA
DA
 NL
NL
 FI
FI
 FR
FR
 DE
DE
 EL
EL
 IT
IT
 JA
JA
 KO
KO
 NO
NO
 PL
PL
 PT
PT
 RO
RO
 RU
RU
 ES
ES
 SV
SV
 TL
TL
 ID
ID
 LT
LT
 SK
SK
 SL
SL
 VI
VI
 TH
TH
 TR
TR
 AF
AF
 MS
MS
 GA
GA
 BN
BN
 HMN
HMN
 LO
LO
 LA
LA
 MI
MI
 MN
MN
 NE
NE
 MY
MY
 UZ
UZ






 Actueel nieuws
Actueel nieuws